Jeff Waksman (left), Project Pele program manager for DOD-SCO, and John Wagner, INL director, at the planned testing site. (Photo: DOD)
The Department of Defense announced September 24 that it has broken ground on the site at Idaho National Laboratory’s Critical Infrastructure Test Range Complex (CITRC) where Project Pele, a transportable 1–5 MWe microreactor, will be tested. The DOD’s Strategic Capabilities Office (SCO) is in charge, on a mission to prove that a mobile microreactor can help meet the DOD’s increasing demand for resilient carbon-free energy for mission-critical operations in remote and austere environments.
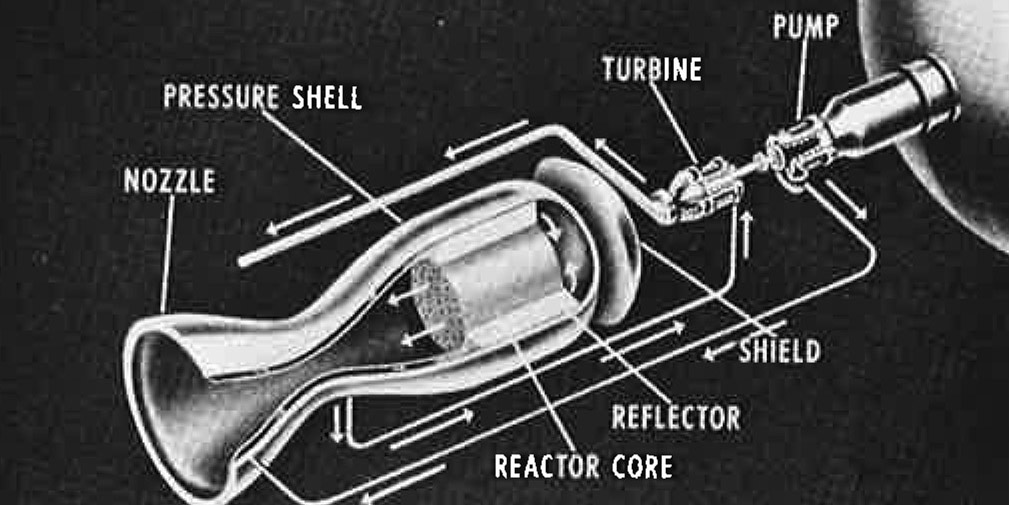
A diagram from the January 1963 story depicting a nuclear-powered rocket.
It’s Thursday, meaning it’s time to dig through the Nuclear News archives for another #ThrowbackThursday post. Today’s story goes back 60 years to the January 1963 issue of NN and the cover story “Review of Rover: A nuclear rocket” (p. 9), which reviews the first phase of the nuclear rocket program from Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Some quick digging online uncovers a lot of information about Project Rover, most notably, a short 20-minute film on the LANL YouTube page that reviews the project (Historic 1960s Film Describes Project Rover). The description of the video notes that the project was active from 1955 to 1973 and led to the design of multiple reactors suitable for testing, including Pewee 1, and that NASA has a modern nuclear thermal propulsion project based on the Pewee design. So it seems fitting to revisit Project Rover, given that there is today a lot of renewed interest in nuclear propulsion for space exploration.
The opening line from the January 1963 article seems to ring true today— “Provided the U. S. continues her space efforts, nuclear-powered rockets are inevitable”—although that probably didn’t seem likely to the nuclear community after the country’s attention shifted from the Space Race to the Vietnam War in the early 1970s when Project Rover was canceled. The introduction to the article lays out the argument for a nuclear-powered rocket and provides a review of the program since its launch in 1955.
The full article as it appeared in 1963 is reprinted below, but don’t forget, all ANS members have full access to the Nuclear News archives that has decades of great content about all topics on nuclear science and technology. Happy reading!
Aircraft line the runway at Eielson AFB in December 2020. (Photo: U.S. Air Force/Senior Airman Keith Holcomb)
The Department of the Air Force and the Defense Logistics Agency–Energy have released a request for proposals (RFP) for the construction and operation of a microreactor in central Alaska. The Department of Defense wants a 20-year supply of electricity and steam from a 1–5-MW microreactor, but the Eielson Air Force Base (AFB) Microreactor Pilot Program will go beyond a simple power purchase agreement and put the reactor through its paces with tests, at least annually, of the reactor’s walk-away safety and black-start capabilities. The final RFP is available at sam.gov.
Artist’s rendering of BWXT’s Project Pele transportable reactor modules arriving for set up and operation. (Image: BWXT)
BWX Technologies, Inc., will deliver the first microreactor in the United States under a contract awarded by the U.S. Department of Defense Strategic Capabilities Office (SCO), the company announced today. BWXT will have two years to build a transportable microreactor prototype to the SCO’s Project Pele specifications and deliver it to Idaho National Laboratory for testing under a cost-type contract valued at about $300 million.
The Project Pele microreactor will be fueled by TRISO fuel particles like those shown here. (Photo: INL)
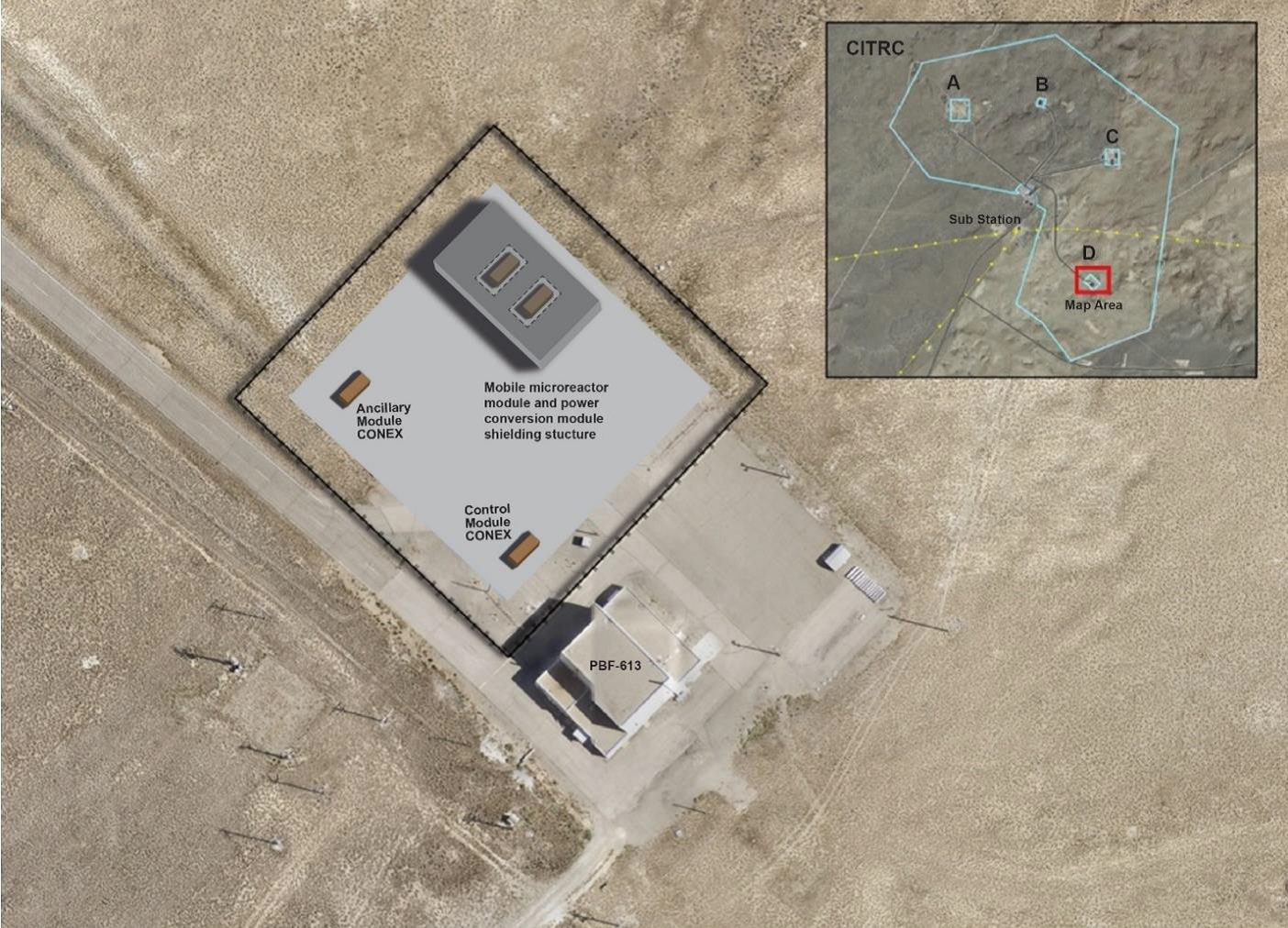
An illustration of a potential mobile microreactor site at Test Pad D in INL’s Critical Infrastructure Test Range Complex for the grid operation phase of Project Pele. (Image: DOD)
The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) is looking to reduce its reliance on local electric grids and diesel-fueled generators at military installations. Project Pele is designed to demonstrate the technical and safety features of mobile microreactors capable of generating up to 5 MWe.
Artist's rendition of the Versatile Test Reactor. (Source: DOE)
An F-35A Lightning II takes off from Eielson Air Force Base in Alaska on July 1, 2021. (Photo: U.S. Air Force/Airman 1st Class Jose Miguel T. Tamondong)
The Department of the Air Force has selected Eielson Air Force Base as the site of a stationary microreactor that “will provide the installation with a clean, reliable, and resilient nuclear energy supply technology for critical national security infrastructure,” the department announced on October 15.
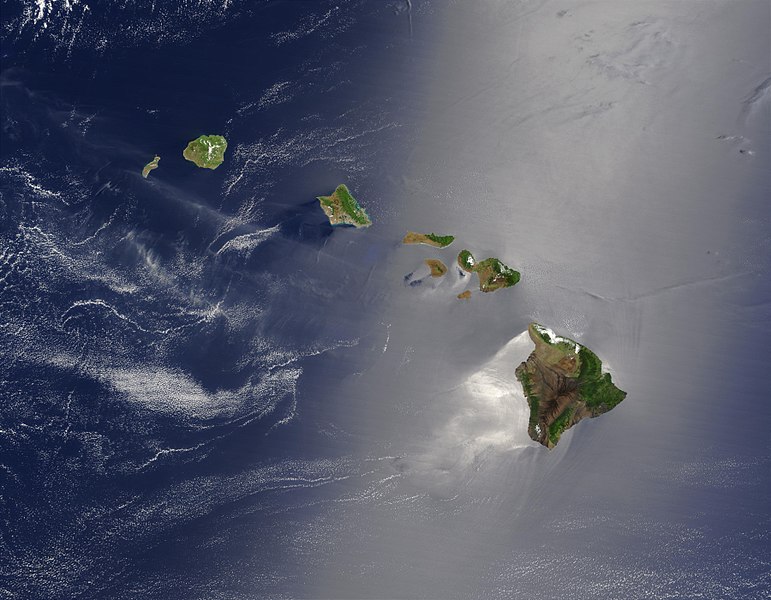
A satellite image of Hawaii. Image: NASA
Jacob Wiencek, a self-described concerned resident of Honolulu, is doing his part to encourage the state of Hawaii to embrace nuclear power. An opinion piece written by Wiencek was published in Honolulu Civil Beat, an online, nonprofit news site, on August 4.